Blockchain technology has been a buzzword in the tech world for the past decade. From its inception with Bitcoin to its current applications in various industries, blockchain is transforming the way we think about data, transactions, and trust. In this article, we will delve deep into what blockchain technology is, how it works, its benefits, applications, and future potential.
What is Blockchain Technology?
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across many computers so that the record cannot be altered retroactively without the alteration of all subsequent blocks and the consensus of the network. This technology ensures transparency and security, making it a revolutionary tool in the digital age.
The History of Blockchain
In 2008, the concept of blockchain was first introduced by an anonymous person (or group) known as Satoshi Nakamoto.1 Nakamoto’s whitepaper, titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System,” laid the foundation for the development of Bitcoin and the underlying blockchain technology. Since then, blockchain has evolved beyond cryptocurrencies, finding applications in various sectors.
How Does Blockchain Work?
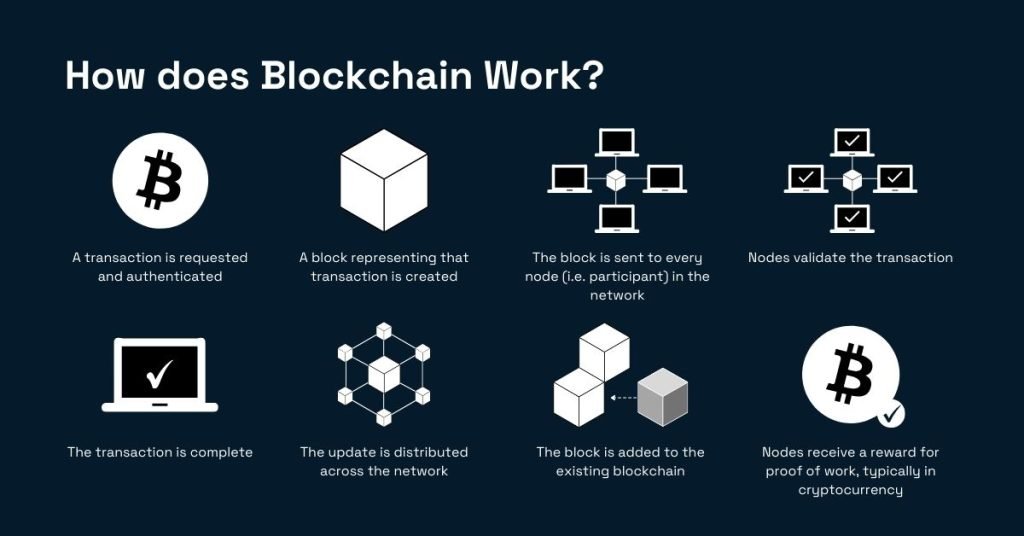
At its core, a blockchain is a chain of blocks, where each block contains a list of transactions. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how it works:
- Transaction Initiation: A transaction is initiated when one party sends information or currency to another.
- Transaction Verification: This transaction is then verified by a network of nodes (computers) through consensus mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS).
- Block Creation: Once verified, the transaction is grouped with other transactions into a block.
- Block Addition: This block is then added to the existing blockchain in a linear, chronological order.
- Immutable Record: The added block cannot be altered, ensuring the integrity and security of the blockchain.
Key Features of Blockchain
Decentralization
In the context of blockchain technology, decentralization2 refers to the distribution of computing power and decision-making authority across a network of nodes or participants. Instead of relying on a single centralized authority (like a government or a company), blockchain networks operate through consensus among their distributed participants.

Transparency
Transparency in blockchain refers to the inherent visibility and openness of the distributed ledger technology. Unlike centralized systems where a central authority controls and validates transactions, blockchain operates on a decentralized network.
Security

Blockchain uses cryptographic algorithms to secure data. Each block is linked to the previous one through a cryptographic hash, making it virtually impossible to alter data without being detected. This high level of Security is one of blockchain’s most significant advantages.
Immutability

Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This Immutability ensures the integrity and reliability of the data, making blockchain an ideal solution for record-keeping.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
Cryptocurrencies
The most well-known application of blockchain is in the creation and operation of Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. These digital currencies use blockchain to ensure secure, transparent, and decentralized transactions.
Supply Chain Management
Blockchain can revolutionize Supply Chain Management by providing a transparent and immutable record of every transaction. This can help track the journey of products from origin to consumer, reducing fraud and increasing efficiency.
Healthcare
In the Healthcare industry, blockchain can be used to securely store and share patient records, ensuring privacy and accuracy. This can streamline processes and improve patient outcomes.
Finance
The Financial sector can benefit from blockchain through faster and more secure transactions, reduced costs, and improved compliance. Blockchain can also facilitate cross-border payments and smart contracts, enhancing the efficiency of financial services.
Real Estate
Real Estate transactions can be made more transparent and secure with blockchain. It can help verify property ownership, streamline the buying and selling process, and reduce fraud.
Voting
Blockchain technology can ensure secure and transparent voting systems. It can prevent election fraud, increase voter turnout, and provide an immutable record of votes.
Benefits of Blockchain Technology
Enhanced Security
Blockchain’s cryptographic security measures ensure that data is secure and tamper-proof. This makes it an ideal solution for industries where data integrity is crucial.
Increased Efficiency
By eliminating intermediaries and automating processes, blockchain can significantly increase the Efficiency of transactions. This is particularly beneficial in sectors like finance and supply chain management.
Cost Reduction
Blockchain can reduce costs by eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing the risk of fraud. This is particularly beneficial for businesses looking to streamline operations and cut expenses.
Improved Transparency
Blockchain provides a transparent and verifiable record of all transactions. This Transparency can build trust among users and stakeholders, making it easier to identify and resolve issues.
Challenges Facing Blockchain Technology
Scalability
One of the biggest challenges facing blockchain technology is Scalability. As the number of transactions increases, the time and resources required to process them also increase. Solutions like sharding and layer-two protocols are being developed to address this issue.
Regulatory Uncertainty
The regulatory landscape for blockchain and cryptocurrencies is still evolving. This Regulatory Uncertainty can hinder the adoption and development of blockchain technology.
Energy Consumption
Blockchain networks, particularly those using Proof of Work (PoW), can consume significant amounts of energy. This Energy Consumption is a concern for sustainability and environmental impact.
The Future of Blockchain Technology
The Future of blockchain technology is promising, with ongoing developments and increasing adoption across various industries. Here are some potential future trends:
Integration with IoT
The integration of blockchain with the Internet of Things (IoT) can create more secure and efficient systems. Blockchain can provide a secure and transparent way to manage IoT devices and data.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is an emerging trend that uses blockchain to offer financial services without intermediaries. This can democratize access to financial services and create more inclusive financial systems.
Enhanced Privacy
Future blockchain developments may focus on enhancing privacy through techniques like zero-knowledge proofs and privacy-focused blockchains. These advancements can ensure that data remains private while still being verifiable.
Interoperability
Interoperability between different blockchain networks is a key focus area. Improved Interoperability can facilitate seamless communication and transactions between various blockchain platforms.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is a revolutionary innovation with the potential to transform various industries. Its key features, such as decentralization, transparency, security, and immutability, make it an ideal solution for many applications. However, challenges like scalability, regulatory uncertainty, energy consumption, and adoption need to be addressed for its widespread use. As technology continues to evolve, the future of blockchain looks promising, with exciting developments on the horizon.
By understanding and leveraging blockchain technology, businesses and individuals can unlock new opportunities and drive innovation in the digital age. Whether it’s through cryptocurrencies, supply chain management, healthcare, finance, real estate, or voting systems, blockchain is poised to redefine the way we interact with and trust digital information.You can learn more about Block Chain here https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Blockchain


